Did Ancient Japanese Fishermen Reach South America 5,000-Years-Ago?

The notion that pre-Columbian cultures from Europe, Africa, or Asia sailed across the Atlantic and Pacific oceans to discover America, is a popular theory backed by numerous books and television documentaries. While most of these claims seem baseless, one theory did gain some credibility, in that it was backed by a reputable archaeologist from the esteemed Smithsonian Institution, the so-called ‘Jōmon-Valdivia hypothesis’. Until recently, mainstream historians and archaeologists most often shunned ideas about ancient transcontinental oceanic travel and the entire notion was considered as pseudoscience. Even in the face of new findings around the world that support the idea that oceans were travelled by ancient peoples who had both the motivation, and means to do so, many archaeologists still refuse to engage with the term “ancient transoceanic voyage.” And this is not as dogmatic as one might at first think, for the history of the subject is infected with mistakes, misinterpretations, and hoaxes that have left trails of confusion in their wake.
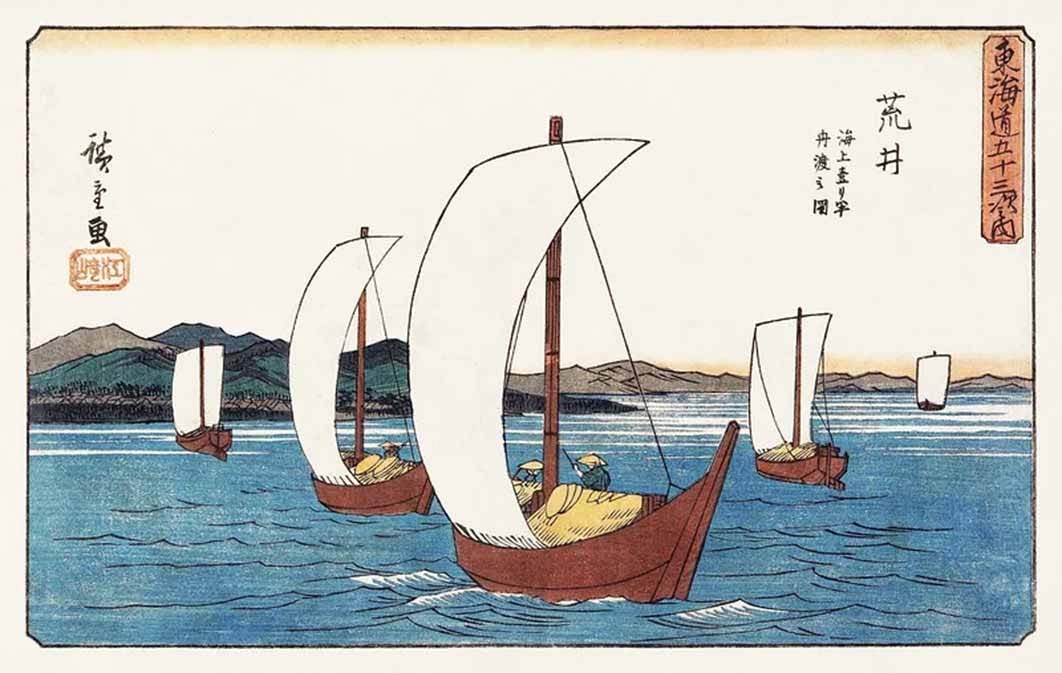
Some theorists suggest that the lost tribes from Israel appeared in North America, or that Phoenicians made it to Lake Titicaca in Bolivia, but no one story has left such a wake of confusion as the ‘Jōmon-Valdivia hypothesis’, a 50-year long archaeological delusion that suggested the ancient peoples of Ecuador did not develop their own culture, but that they inherited it from prehistoric fishermen from Japan around 3000 BC.

